
Setianingsih
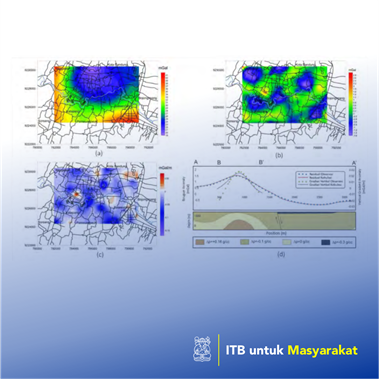
One of the causes of the land subsidence phenomenon is the excessive use of groundwater. This will cause a material emptiness in the aquifer zone, so that it becomes compressed and compacted, and in turn will cause a subsidence on the ground surface land. Groundwater level monitoring in the Bandung Basin area has been carried out since the early 2000s until 2019 and concluded that the land subsidence has occurred in the Bandung Basin area, including Cimahi, Gedebage, Majalaya, and Dayeuh Kolot. From the results of GPS measurements, it can be concluded that there has been a decrease in the land surface by 4 cm to 14 cm per year (Gumilar et al., 2012). In this research, forward modeling of gravity data is carried out to determine the response of Bouguer gravity anomaly and vertical gravity gradient anomaly caused by an anomaly source. Based on these results, it can be identified the comparation result of forward modeling responses of Bouguer gravity anomaly and vertical gravity gradient anomaly caused by several sources of varying anomaly depth and contrast density (for representing the existence of compaction zone). The field gravity data that have been obtained are then processed to obtain the complete Bouguer, regional-residual, and the vertical gravity gradient anomalies. The measurements of the vertical gravity gradient method were carried out by measuring the gravity value at two different heights at the same measurement point.
Penerapan Karya Tulis
Bandung is one of the cities in Indonesia which is located in the Bandung Basin area that has a very massive land subsidence phenomenon. Some factors of land subsidence in this area is due to excessive groundwater extraction which causes the phenomenon of compaction in aquifers (Gumilar et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2012). The use of the gravity method in this study aims to identify the existence of subsurface compaction zones at shallow depths and to determine the subsurface geological structures. The combination of residual Bouguer gravity method and the vertical gravity gradient method is expected to minimize the ambiguity and limitations of the two methods.