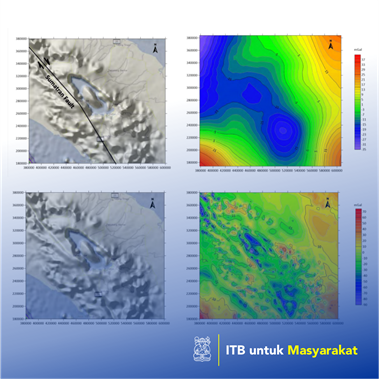

Dadi Abdurrahman
Gravity data represents an image of subsurface. This data can be obtained from land, marine, airborne, and satellite data. Each of these data has its advantages and limitations. Land data usually have distances between stations ranging from tens of meters to kilometers. Generally, this survey conducted for preliminary measurements to the detailed stage, both for geotechnical and environmental purposes (Adams, WM, 1984; Arzi, AA, 1975; Benson, et al, 1983; Butler, DK, 1984), oil and gas industry (Liu L, 2018), geothermal (Zaher MA, et. al., 2018) and mining (Chen, GX, et. al., 2015; Dransfield, MH, 2007). Marine gravity data is carried out to determine the distribution of gravity values in the ocean area, usually using a boat either directly above it or placing a gravimeter on the ocean floor. In this research, the author tries to use gravity satellite data which can be downloaded from the site https://topex.ucsd.edu/cgi- bin/get_data.cgi . The data on the site can be downloaded for free. The author tries to use this data in the Lake Toba area, North Sumatra.
Penerapan Karya Tulis
Airborne gravity data (Moore D, et. Al., 2013) is generally carried out for areas that are difficult to reach by land. Generally, this data collection is very fast and wider than land measurements. Gravity satellite data is rarely used because of technological factors that make the data expensive. This data usually has a very wide range, but the spacing between the data is not so tight. Taking into account the advantage of satellite data that is able to cover a very wide area, it would be very good if this data was used to study subsurface conditions that are very regional and deep, such as tectonic studies (Qu NN, et. Al., 2018), volcanoes and faults which are very deep and long.