
Akhmad Riqqi
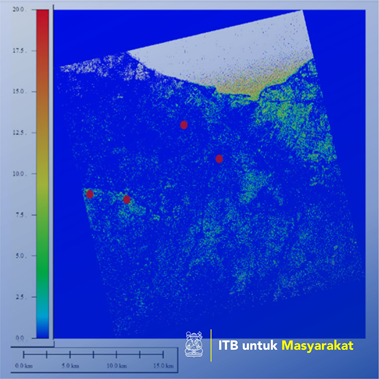
Microwave backscattering from the earth’s surface depends on several parameters such as surface roughness and dielectric constant of surface materials. The two parameters related to water content and porosity are crucial for estimating soil moisture. Basic to the soil moisture is the knowledge of its permittivity (dielectric constant). Radar scattering by a bare soil surface is determined by the geometry of soil surface, commonly known as surface roughness and dielectric properties on the soil, which depends on soil characteristics such as moisture, particle-size distribution and mineralogy (Wang, L, 2009) . Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors have a high potential to measure surface soil moisture (Baghdadi et al., 2012). It is also known that the SAR signal back above bare soil surface is influenced by characteristics such as surface roughness and dielectric constant ground (A.K.Fung, 1994). The expected results of this research is dielectric constant modeling using Radarsat-2 Image as parameters to determine soil moisture value. Visually to distinguish objects containing water and not, the image of RADARSAT-2 made in the form of color using Decompotition Freeman (Figure 2). Dark color indicates the object containing water. Figure-3 shows the dielectric constant resulting from RADARSAT-2 imagery using Dubois models. The red circle shows the correlation between objects containing water with dielectric constant. Mapping constanta dielektric using field data has been reliable and constanta dielectric measurement itself is not practical and not feasible for large-scale applications. In this study, a method was developed to map the characteristics of constanta dielectric parameters using RADARSAT-2 for minimize the field data collected. The constanta dielektric models have not validated yet against field measurements.
Pelaksanaan Kegiatan Kepedulian Sosial berupa pendidikan/penyuluhan/pendampingan
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors have a high potential to measure surface soil moisture (Baghdadi et al., 2012). It is also known that the SAR signal back above bare soil surface is influenced by characteristics such as surface roughness and dielectric constant ground (A.K.Fung, 1994).